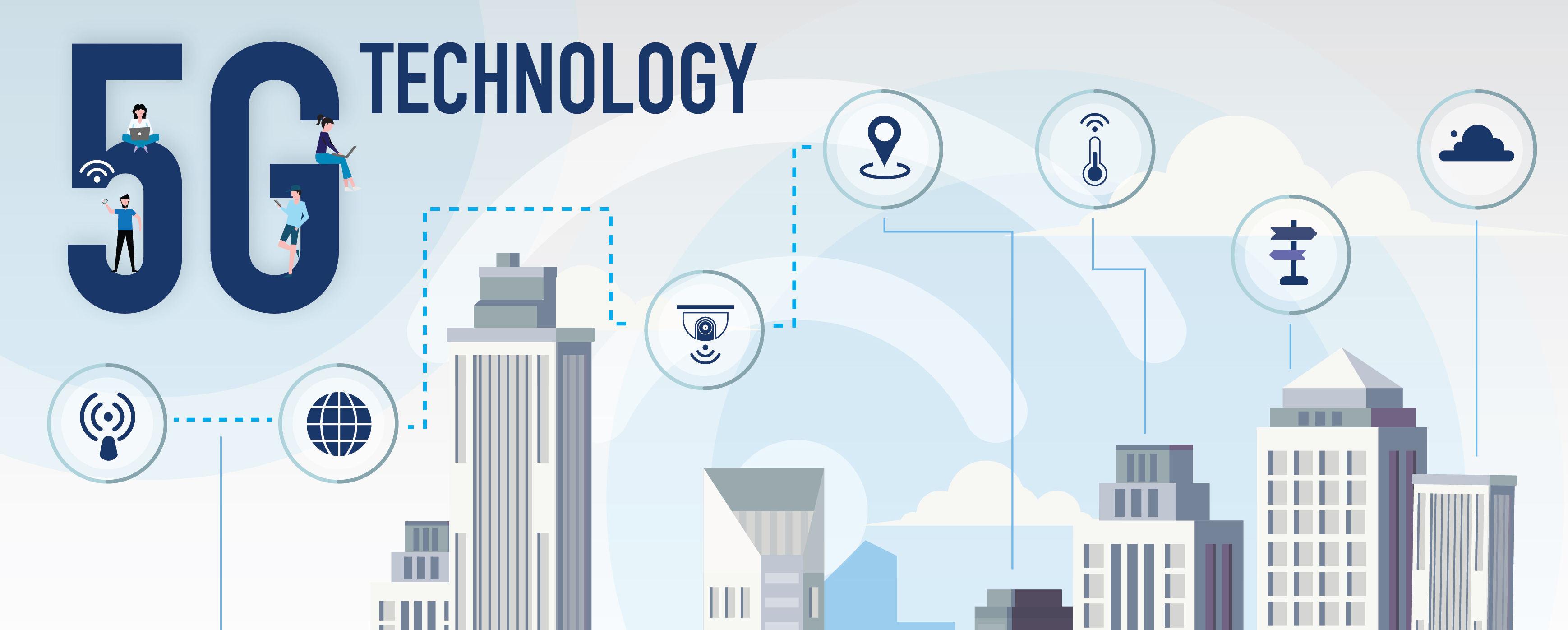
The fifth-generation wireless technology, commonly known as 5G, has ushered in a new era of connectivity, promising faster speeds, lower latency, and a plethora of opportunities for innovation across various industries. This transformative technology promises to redefine the way we connect, communicate, and experience the digital world.
In this blog post, we will explore the intricacies of The fifth-generation wireless technology, covering its key features, potential applications, challenges, global rollout, and the profound impact it is set to have on various industries.
Understanding 5G Technology:
Speed and Low Latency:
5G boasts remarkable speed, offering gigabit-per-second download rates. This unprecedented speed is complemented by significantly lower latency, ensuring minimal delays in data transmission. This opens the door to real-time applications and a more responsive digital experience.
Frequency Bands:
Unlike its predecessors, 5G operates on a broader spectrum of frequency bands, including high-frequency millimeter waves. This extended range enables higher data rates, increased network capacity, and improved overall performance.
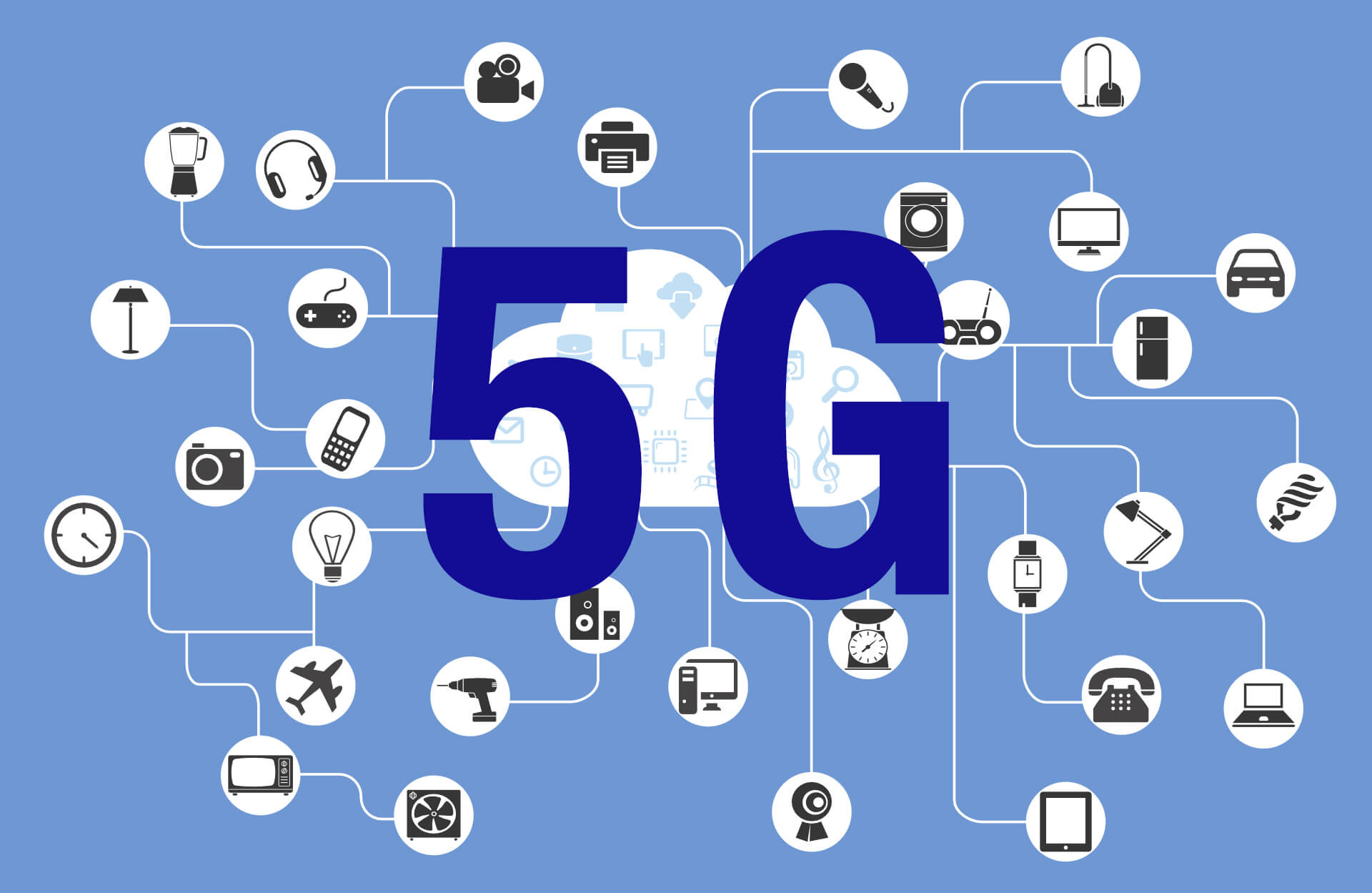
Applications Across Industries:
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB):
The improved mobile broadband experience provided by 5G allows users to stream high-definition content, engage in virtual reality experiences, and enjoy seamless connectivity in densely populated areas.
Internet of Things (IoT):
5G’s extensive connectivity is a catalyst for IoT applications, facilitating the deployment of a myriad of devices. From smart cities to connected vehicles and industrial automation, 5G enables reliable and low-latency communication for a wide range of IoT applications.
Healthcare Innovations:
The healthcare sector stands to benefit significantly from 5G, with applications such as remote patient monitoring, augmented reality for surgeries, and rapid transfer of large medical data files revolutionizing the industry.

Challenges and Considerations:
Infrastructure Requirements:
The implementation of 5G necessitates a substantial upgrade to existing infrastructure, including the installation of new base stations and the deployment of small cells to support the increased demand for connectivity.
Security Concerns:
As connectivity increases, so does the potential for cyber threats. Addressing security challenges is crucial to ensuring the integrity and privacy of data transmitted over 5G networks.
